The core of Interface Management is to maintain a central inventory of interfaces which is also called Interface Inventory, Catalog, Repository, Library or Asset Management. All mean the same thing: To centralize enterprise integration knowledge, having a common place for all your companies integrations (not only APIs and Events).
This ideally works fully automated, reading interface configurations and traffic data from for SAP, Microsoft Azure, Solace, Kafka, MuleSoft, and beyond. An inventory provides an option to also enrich data with your own knowledge and work on the insights from this combined data.
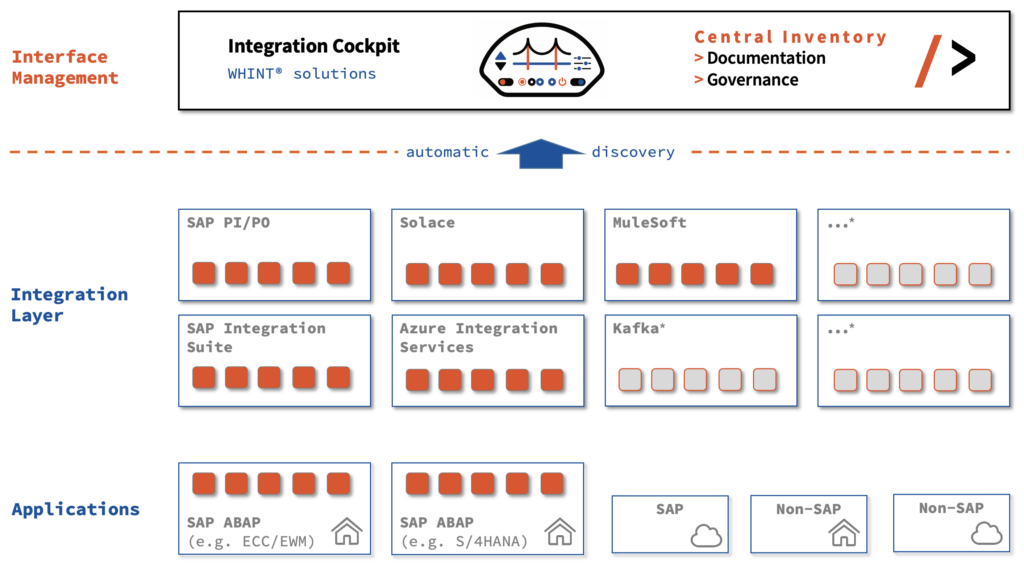
Also, this automatically discovered interfaces can feed your Enterprise Architecture Management System, such as SAP LeanIX, LUY, Mega Hopex or Bee360 EAM. Our Integration Cockpit acts as a consolidation layer to manage discovered (technical) interfaces in the context of End-to-End Integrations.
One goal is to be prepared for the next project (new application, merger/carve-out, release change, new law, larger transformation). However, visibility to stakeholders (IT management, project management, business) is also very important to position Enterprise Integration within the organization more strategically, from technical “plumbing” to organized and governed integration excellence.
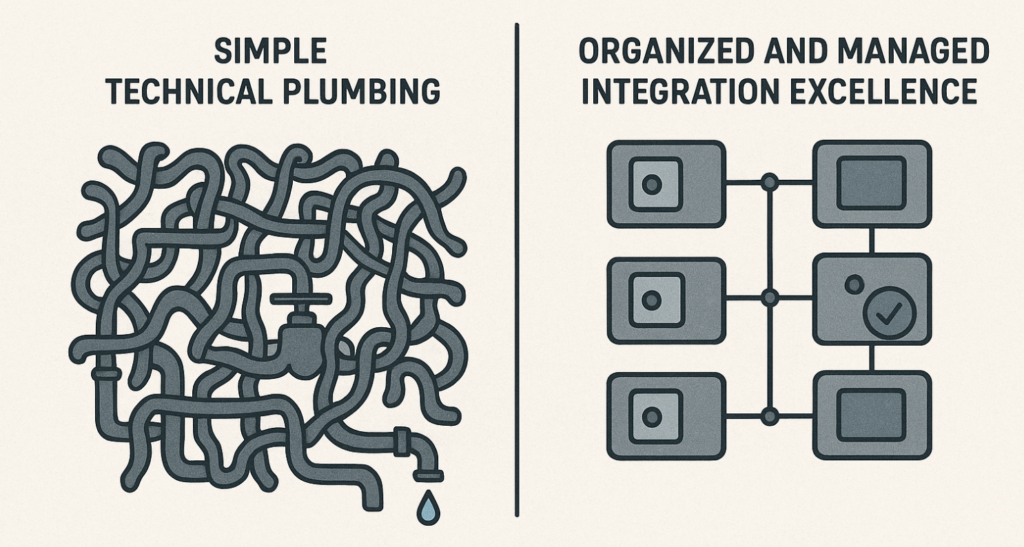
Having visibility / transparency about enterprise integration is not only about Operational Control (this is addressed with monitoring tools), but about:
- Impact Analysis & Change Management (what if we replace an application, how do we support projects, e.g. rollouts & testing)
- Governance (who owns what, what data is exchanged, …)
- Optimization & Rationalization (identify redundant/obsolete, support modernization)
- Strategic Decision-Making (which interfaces support business capabilities)
- Collaboration (supports a common language and increases accountability & ownership)
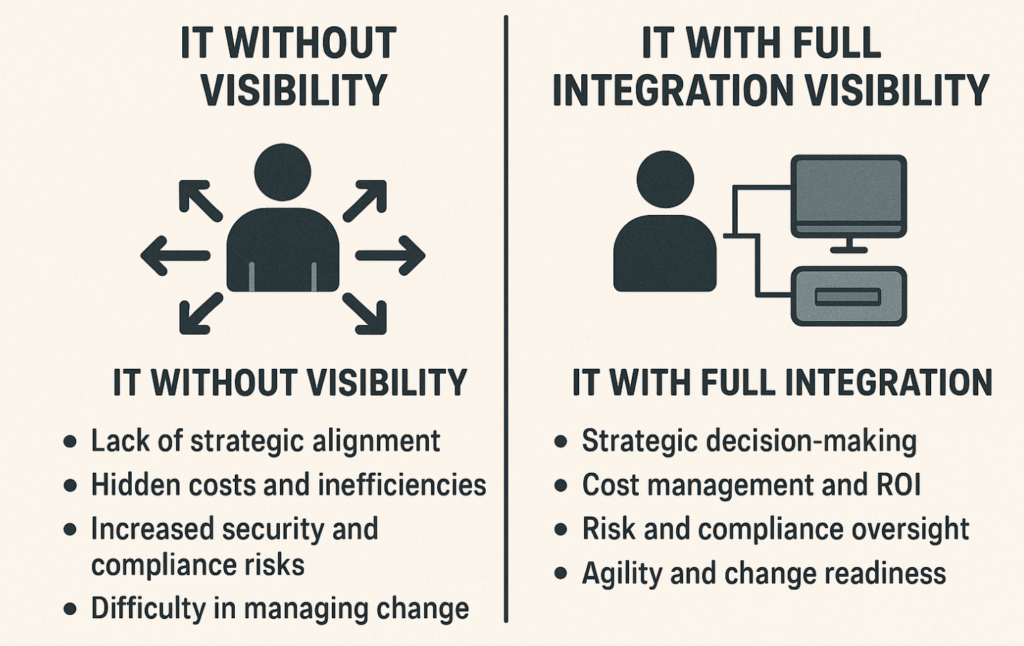
IT management specifically benefits from the following insights:
Visibility turns integrations from a technical detail into a strategic asset.
It enables control, transparency, cost efficiency, and agility — the foundations of mature IT governance:
- Strategic Alignment & Decision-Making (supports enterprise architecture & digital strategy)
- Cost Management (quantify integration costs)
- Risk & Compliance (see dependencies, security elements, ensure audit readiness)
- Operational Performance & Reliability (proactive interface operations)
- Accountability & Governance (ownership & quality gates)
- Agility & Change Readiness (plan changes faster)